2. Inside View of Japanese Industry
@26/Jan/2005
RSS Eurasia Club/JICA SV in RSS Amman Jordan
Purposes, Coordinator Office, Schedule, Materials, Top
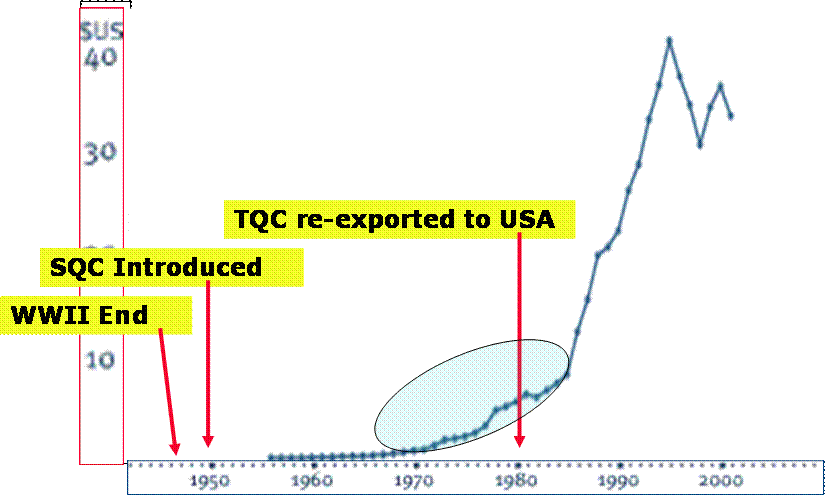
Relation between QC activity and income increase
1. Prologue
After the complete corruption of Japanese industry and prohibition of recovery on heavy industry brought by the World War II that ended in 1945, industrial leaders in Japan hectically struggled the way the country could live on.
Under the total ban of heavy industry by the occupation authority, only light industries, like textile and living commodities.
These were the products we could export to purchase the badly needed hard currency to import fuel and other low materials for almost every field of industries that we do not have at all in Japan. Without import of these basic materials, Japan could not live even for a day. Therefore, purchasing hard currencies by exporting home made products was essential.
2. Strategy
To gain the hard currencies more effectively, more value added high quality products shall be developed and produced in lower price, and in faster delivery time.
High Performances
Low Price
Fast Delivery
Industrial Leaders had firm confidence that the quality is the most important factor to remain competitive in the harsh international market.
3. Roll out
Kaizen
(Improvement) activities was taken as a common practice everyindustry all over Japan, from the
heavy industry to the service industry in all
working level from president to assembly worker. Penetration of this
practice to the Japanese industry was so extensive. Every small or big
improvement on any procces is welcomed, resistered and put into operation
whatever the idea was thought effective for producing better products or
services for human being, or effective for easing gloval environment. Thanks to
the great success of this practice, Kaizen became the important and common
International jargon in the every field of industrialimprovement.
Now, there are some figures how this Kaizen activity is really working.
Panasonic: 670,000 Kaizen suggestions/year
Toyota: 360,000 Kaizen suggestions/year
Toshiba: 1,080,000 Kaizen suggestions/year
Sumitomo Metal: 650,000 Kaizen suggestions/year
Matsuda: 190,000 Kaizen suggestions/year
GM: 350,000 Kaizen suggestions/year
IBM: 100,000 Kaizen suggestions/year
4. Tools
To gain the maximum output from the Kaizen Ativities, following tools were employed at all level of workers and management, including management, planning, development, design, production, logistics, finacing and sales. The main points were;
Everyone’s Participation
Small Group Activity
5S
Visual Management
|
[Purposes] [Coordinator Office] [Schedule] [Materials] [Top] |