7. Railway System in Japan
Shinkansen
@27/Jul/2005
RSS Eurasia Club/JICA SV in RSS Amman Jordan
[Purposes] [Coordinator Office] [Schedule] [Materials] [Top]
1. Abstract:
Japanese Railway System is almost mystically believed of its punctuality in extreme dense packed traffic. Japan has developed its railway system into state of art standard of efficiency and safety in order to handle the demanding traffic in densely populated metropolitan area like Tokyo and Osaka. This tradition to keep punctuality become heavy burden for the train operating company and its workers. Time table of the train traffic becomes more and more congested. In some cases, every scores of seconds, another train depart from the same platform. That requires extra stress to the train driver to keep the time table in as short as seconds. Delay of the train for few tens of seconds usually does not considered in anywhere in the world except Japan. Today, railway in Japan stretches 32,674km throughout Japan, carrying 60 million people each day.
In 1950s, the train system was losing its interest by travellers in every
part of the world. Because of its limited mobility, comfort and speed.
Short distant travellers prefer automobile and long distant travellers
prefer airplane than taking train. However, in this adverse worldwide trend,
Japan had developed high speed train system and put it into operation by 1964, commemorating the Tokyo Olympic Game. Decision of building the high speed train system, and very short period of development and construction in 5 years of 552km long Tokaidou-Shinkansen Line was really unique and admirable
achievement.
So called bullet train was really innovative that no one in Europe and USA could expect the realization such high speed train at that time Targeted and achieved speed of the train was more than twice the speed of the conventional fasted train in Japan. Fastest conventional train at that time travels in 95km/h, instead the Bullet Train travels in 210km/h all the way. This success of high speed train made renaissance of high
speed rail way transportation era in the western countries like France
and Germany in short period They changed their mind that train is still
useful for mass public transportation.. Thus, French TGV, German ICE was built after the success of Shinkansen(Bullet Train) in Japan.

Shinkansen (MAX Yamabiko)
2. Technologies used in Shinkansen:
Dozen of new technologies are used in Shinkansen to achieve its targeted speed, passenger's comfort and safety. Those are;
_____1. Long rail: 1.5 km rail instead of 25m conventional
_____2. No crossing (All exclusive or elevated track)
_____3. Air tight Body (Avoid rapid pressure change in Tunnels)
_____4. Anti-vibration by Air Spring
_____5. No signal on the track, but on Driver's Seat
_____6. CTC (Centralized Traffic Control) controls all traffic
_____7. Anti-collision System keeps train 3km or more at all time
_____8. Fed by AC 25,000 V instead of conventional DC 1,500 V
_____9. All Motored Car with newly developed extra quiet motors
____10. Half size Pantograph reduced air resistance
____11. Placed Emergency Stop Switch every 250m along the track
____12. Earthquake Detection System stop feeding on detecting the quake
2.1 Long Rail:
Conventional rail is approx. 25 m long, instead, Shinkansen uses long rail
of approx. 1.5 km. So that annoying click sound is greatly reduced in order
to secure comfort of travellers. Further more, at connection part it employs
gap-less sliding cut shown in the figure below.


Joint Section of the Long Rail
2.2 No Crossing (All exclusive or elevated Track):
Tracks for Shinkansen were newly constructed as exclusive use, and in all
metropolitan area, elevated tracks are used in order to secure the safety
for other transportation means and trespassers. Specially designed fences
are installed on the platform of Shinkansen Railway Station to prevent
accident that people collides with passing train on its maximum speed even
in the premises of the station.

Exclusive use tracks, or in metropolitan area all tracks are elevated
2.3 Air-tight Body:
Due to geographical landscape that Japan has, railway track should have
many tunnels through its line. When high speed train got into the tunnel,
air pressure rapidly changes and passenger suffer sever uncomfortable ear-ache
every time the train passes the tunnel. In order to avoid such suffering,
the body is made air-tight design similar to airplane, so that the air
pressure is kept constant whenever the train passes the tunnel.

Interior of Shinkansen passenger car
2.4 Anti-Vibration of the Body:
When the train travel in high speed, the body starts shaking, and in the
worst case, it would be disintegrated. To prevent this body vibration,
air spring was newly developed to be installed in all car. Smooth and quietness
in the passenger car is achieved. Improvement of this technology is ever
developed and implemented into the passenger car, so that travellers can
enjoy quieter and smoother passenger car year by year.
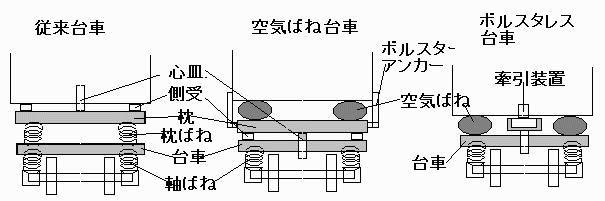
Above drawings shows very simplified principle of air spring. Today, this
air spring is highly developed and modified, and transformed into active
suspension system which control position of whole body and individual passenger
seat against bending G and horizontal/vertical vibration of the passenger
car.
2.5 No signal post on the track but on Driver's Seat:
Since the Shinkansen travels at high speed of 270km/h or more, the driver could not see the ordinal signal posted on the signal post along the track. So that no signal post is place along the track, instead all necessary signal are displayed on the driver's seat. The signal is sent from CTC (Centralized Traffic Control Center) via railway.

All necessary signals are displayed on Driver's Seat, but no signal along
the track
2.6 CTC (Centralized Traffic Control System) controls all traffic:
Because of the safety is the most important factor in the high speed train
system, Central Traffic Control System (CTC) is newly developed and introduced.
Ordinal control system by communicating central controller and train driver
could not work in high speed train system due to shortage of time to judge
the necessary action and convey it to the train driver in time.


CTC old (Left) and new (Right)
CTC in the beginning was displayed on a large wall-type display, but today,
it is displayed in more compact and advanced PC display.
2.7 Anti-collision System:
One of the safety measures taken is anti-collision system. This system
works to keep train distance 3km or more at any time. When the train approaches
other train and its distance becomes 3km, the system automatically reduces
the speed of the train down to 30 km/h and the tragic collision accident
shall be prevented.
2.8 Fed by AC 25,000 V:
Conventional train is fed by DC 1,500 V, instead Shinkansen is fed by AC
25,000 V in order to reduce the construction cost of feeding line along
the railway track. In higher voltage, thinner feeding line can be used.
As for the car design, using higher voltage can reduce the total weight
and increase the speed. Only two Pantograph are necessary in one whole
train which greatly reduce the air resistance and air cutting noise. Thus
it contributes to the environmental friend design as well.
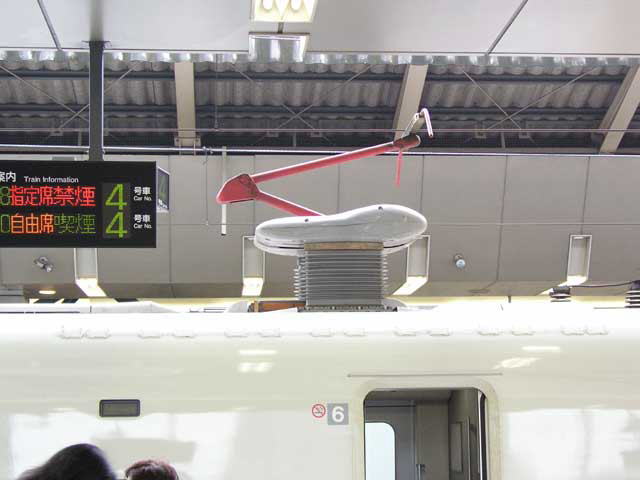

One arm Pantograph: only two pantographs are necessary for one whole train (8 to 16 cars)
Shape of the pantograph is designed aerodynamically, and reduced air cutting
noise in minimum.
2.9 All car has Motors:
It was long legendary concept that the long-distance passenger car is pulled
by heavy locomotive(s) in order to secure quietness and give comfort to
the passengers. Idea of all motored car in luxurious long distance passenger
car was unprecedented. But Japanese railway engineers reached their conclusion
that all motored car is the solution to raise the speed more than twice
than that of the maximum speed of that time. Engineers had believed that
breakthrough could be made to reduce the mechanical noise of motor to the
level of normal saloon car even before they start research and development.
By putting motors in every car, weight of maximum load to the railway track
greatly reduced and construction cost and delivery time of the railway
track had reduced tremendously.

No locomotive but all car has motors
2.10 Half Size Pantograph:
Size of the pantograph has been reduced in half compared to the conventional
type, so that the air resistance and air-cutting noise had been reduced
considerably. This was achieved by constructing exclusive railway track
for Shinkansen,. the distance between the pantograph and feeding line can
be kept in certain figure at any speed that Shinkansen travels.
2.11 Emergency Stop Switch is located at every 250m along the railway track:
In order to secure maximum safety measures, emergency stop switch is installed
at every 250 m along the railway track from the beginning of the line to
the end of the line.
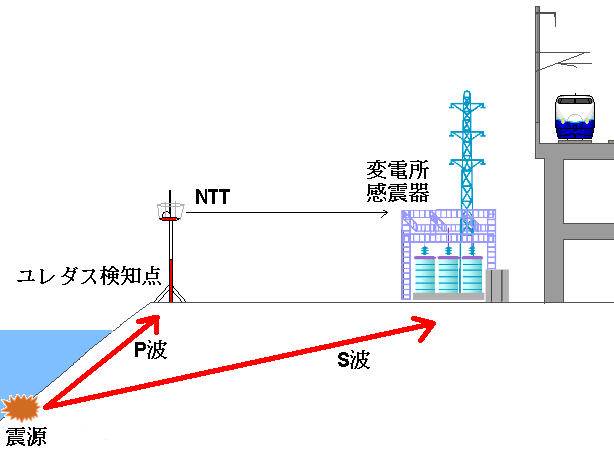
2.12 Earthquake Detection system stop Feeding:
Japan is earthquake rich country. Anti-earthquake system is indispensable
for mass high speed transportation system. In this sense, earthquake detection
system had been developed and put into operation as one of the safety measures
of Shinkansen. When the system located most close to the epicenter detects
P-wave of the earthquake, and it automatically cuts the feeding to the
Shinkansen and stops the train immediately before the S-wave reaches to
the train.
| [Coordinator Office] [Purposes] [Schedule] [Materials] [Top] |
| [Back to Page Top] |